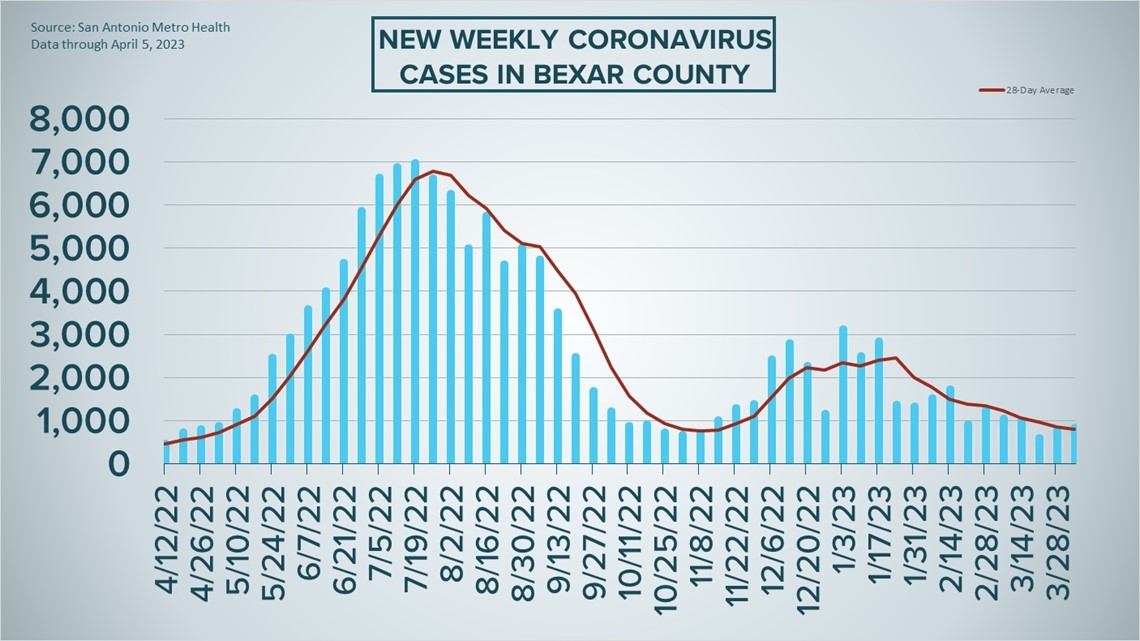
SAN ANTONIO — Fewer coronavirus hospitalizations ensured that the risk level for virus spread in Bexar County remained at "low" for a fourth straight week, though Metro Health did tally a slightly higher number of cases overall.
Health officials recorded 853 new COVID-19 infections in San Antonio for the period starting March 29 and ending on April 5, up from 791 the week prior. The seven-day case average increased as a result from 113 to 122, though the numbers are miniscule compared to when the virus was running rampant.
There were 69 patients receiving treatment for their virus symptoms this week, down from 79 last week. Of those 69 Bexar County patients, 13 were in intensive care.
The next opportunity to get a COVID-19 vaccine at no cost courtesy of Metro Health is Thursday afternoon at a south-side health fair.
More than 697,000 coronavirus infections have been recorded in Bexar County since the pandemic began, though that number likely doesn't include thousands of positive at-home tests that went unreported.
At least 6,220 county residents have died from virus complications, according to Metro Health.
How Bexar County is trending

Vaccine progress in Bexar County
The following numbers are provided by San Antonio Metro Health via this page.
- 74.2% of eligible Bexar County residents (those over 6 months of age) are fully vaccinated as of March 14.
- 14.4% of eligible Bexar County residents (those over 5 years of age) have received a bivalent booster as of March 14.
The CDC states that "when a high percentage of the community is immune to a disease (through vaccination and/or prior illness)," that community will have reached herd immunity, "making the spread of this disease from person to person unlikely."
The City of San Antonio breaks down the vaccination rates by zip code on Metro Health's Vaccination Statistics page.
Coronavirus in Texas
The Texas Department of State Health Services transitioned to weekly COVID-19 reports at the start of 2023, with new data arriving every Wednesday.
For the week of March 30 to April 5, the state reported 12,202 cases; that total includes 6,823 new confirmed cases and 5,379 new probable cases. More details can be found on this page.
Those figures bring the total number of Texans diagnosed with COVID-19 to more than 8.46 million.
Meanwhile, 75 additional virus-related deaths were reported for the last week in Texas. The statewide death toll stands at 92,093. The positivity rate stands at 8.2%, up from 7.79% last week.
Coronavirus symptoms
The symptoms of coronavirus can be similar to the flu or a bad cold. Symptoms include fever or chills, cough, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, fatigue, muscle or body aches, headache, new loss of taste or smell sore throat, congestion or runny nose, nausea or vomiting, and diarrhea, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
Most healthy people will have mild symptoms. A study of more than 72,000 patients by the Centers for Disease Control in China showed 80 percent of the cases there were mild.
But infections can cause pneumonia, severe acute respiratory syndrome, kidney failure, and even death, according to the World Health Organization. Older people with underlying health conditions are most at risk.
Experts determined there was consistent evidence these conditions increase a person's risk, regardless of age:
- Chronic kidney disease
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Obesity (BMI of 30 or higher)
- Immunocompromised state (weakened immune system) from solid organ transplant
- Serious heart conditions, such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, or cardiomyopathies
- Sickle cell disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- The CDC believes symptoms may appear anywhere from two to 14 days after being exposed.
Human coronaviruses are usually spread...
- Between people who are in close contact with one another (within about 6 feet).
- Through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby or possibly be inhaled into the lungs.
- Some recent studies have suggested that COVID-19 may be spread by people who are not showing symptoms.
Help stop the spread of coronavirus
- Stay home when you are sick.
- Eat and sleep separately from your family members
- Use different utensils and dishes
- Cover your cough or sneeze with your arm, not your hand.
- If you use a tissue, throw it in the trash.
Find a testing location
City officials recommend getting a COVID-19 test if you experience fever or chills, cough, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, fatigue, muscle or body aches, headache, new loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion or runny nose, nausea or vomiting, or diarrhea.
Here's a Testing Sites Locator to help you find the testing location closest to you in San Antonio.

