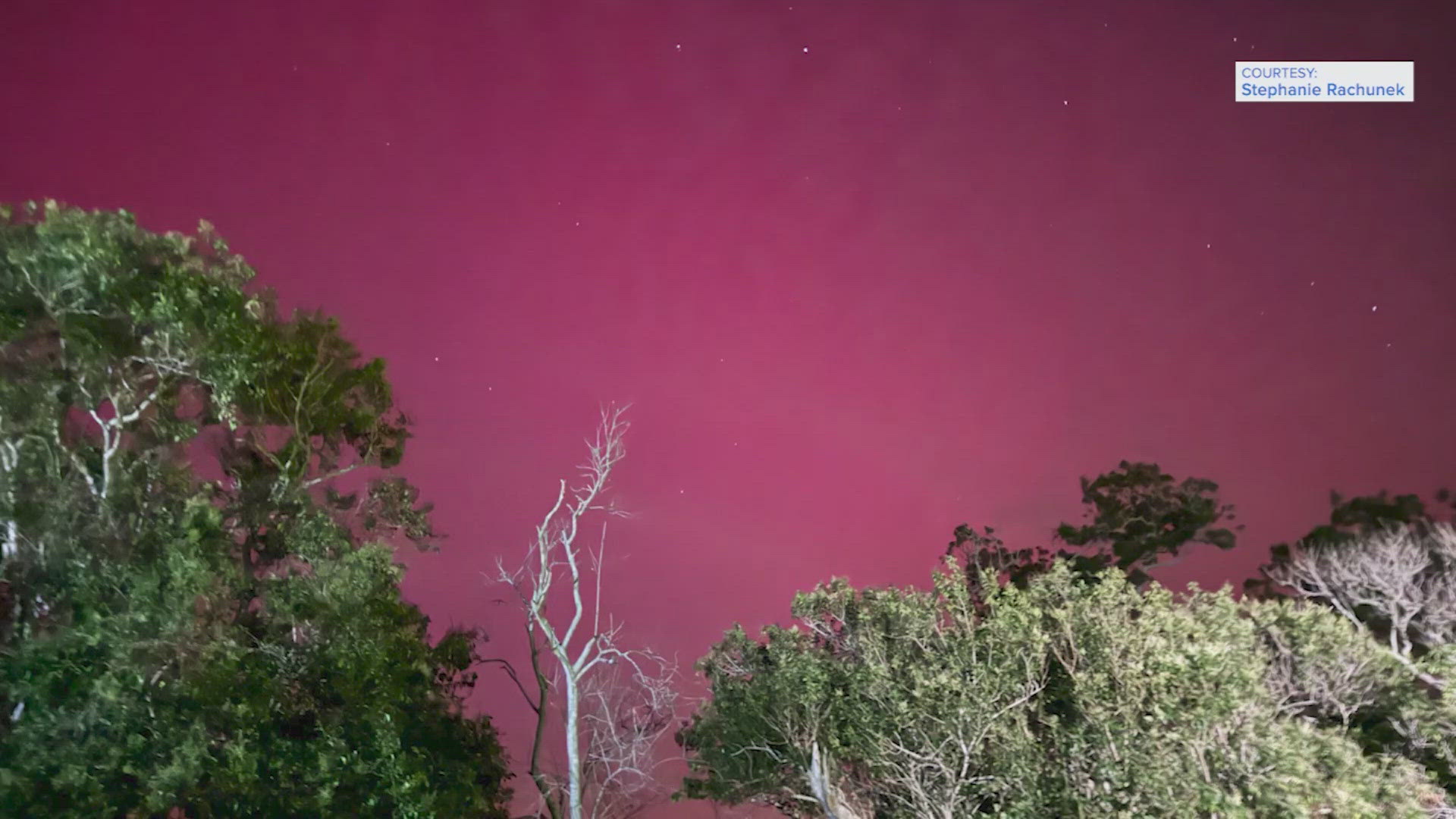
TEXAS, USA — An unusually strong solar storm produced Northern Lights in the U.S. Friday night and they were reportedly even visible from Southeast Texas. So, will the Houston area be able to see them again tonight?
The NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center has the phenomenon peaking in the northern U.S. from about 9 p.m. to 10 p.m. on Saturday. There is a chance it'll be visible in Southeast Texas like Saturday, but the weather may rain on your parade. It may be a cloudy night with isolated storms, which could block any potential view.
Friday night, some parts of the Houston area outside the city could see the glow of the aurora with cameras.
If you have photos, share them with us through the Near Me feature of our news app.
Friday night at 9:38 p.m., the National Weather Service Houston said it was receiving reports of visible aroura in Southeast Texas.
NWS Burlington put out a graphic highlighting the northern lights over North America.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration issued a rare severe geomagnetic storm warning when a solar outburst reached Earth on Friday afternoon, hours sooner than anticipated. The effects were due to last through the weekend and possibly into next week. NOAA alerted operators of power plants and spacecraft in orbit to take precautions, as well as the Federal Emergency Management Agency.

“For most people here on planet Earth, they won’t have to do anything,” said Rob Steenburgh, a scientist with NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center.


If they are visible that far south, experts stressed it would not be the dramatic curtains of color normally associated with the northern lights, but more like splashes of greenish hues.
“That’s really the gift from space weather — the aurora,” said Steenburgh. He and his colleagues said the best aurora views may come from phone cameras, which are better at capturing light than the naked eye.
Snap a picture of the sky and “there might be actually a nice little treat there for you,” said Mike Bettwy, operations chief for the prediction center.


The most intense solar storm in recorded history, in 1859, prompted auroras in central America and possibly even Hawaii. “We are not anticipating that” but it could come close, said NOAA space weather forecaster Shawn Dahl.
This storm — ranked 4 on a scale of 1 to 5 — poses a risk for high-voltage transmission lines for power grids, not the electrical lines ordinarily found in people's homes, Dahl told reporters. Satellites also could be affected, which in turn could disrupt navigation and communication services here on Earth.
An extreme geomagnetic storm in 2003, for example, took out power in Sweden and damaged power transformers in South Africa.
The sun has produced strong solar flares since Wednesday, resulting in at least seven outbursts of plasma. Each eruption — known as a coronal mass ejection — can contain billions of tons of plasma and magnetic field from the sun's outer atmosphere, or corona.
The flares seem to be associated with a sunspot that’s 16 times the diameter of Earth, according to NOAA. It's all part of the solar activity that's ramping up as the sun approaches the peak of its 11-year cycle.
NASA said the storm posed no serious threat to the seven astronauts aboard the International Space Station. The biggest concern is the increased radiation levels, and the crew could move to a better shielded part of the station if necessary, according to Steenburgh.
Increased radiation also could threaten some of NASA's science satellites. Extremely sensitive instruments will be turned off, if necessary, to avoid damage, said Antti Pulkkinen, director of the space agency's heliophysics science division.
Several sun-focused spacecraft are monitoring all the action.
"This is exactly the kinds of things we want to observe,” Pulkkinen said.

