HOUSTON —
EDITOR'S NOTE: This page will no longer be updated. For the latest information on Beryl, please check here.
_______________________
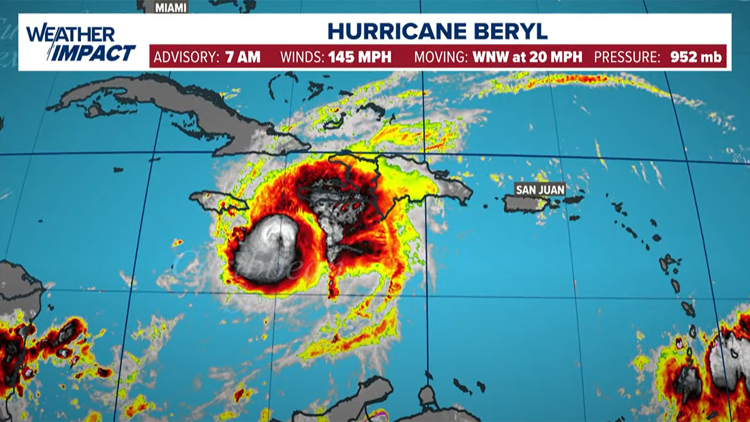
Hurricane Beryl roared through open waters Wednesday as a powerful Category 4 storm heading toward Jamaica after earlier making landfall in the southeast Caribbean, killing at least six people.
A hurricane warning was in effect for Jamaica, Grand Cayman, Little Cayman, Cayman Brac and for Haiti's entire southern coast. Beryl was forecast to start losing intensity on Tuesday but still be near major hurricane strength when it passes near or over Jamaica early Wednesday, near the Cayman Islands on Thursday, and into Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula on Friday, according to the National Hurricane Center.
Late Monday, Beryl became the earliest storm to develop into a Category 5 hurricane in the Atlantic, fueled by record warm waters, though it was downgraded a notch Tuesday to Category 4.
The center said Beryl was expected to bring life-threatening winds and storm surge to Jamaica, where officials warned residents in flood-prone areas to prepare for evacuation.
Weather Impact
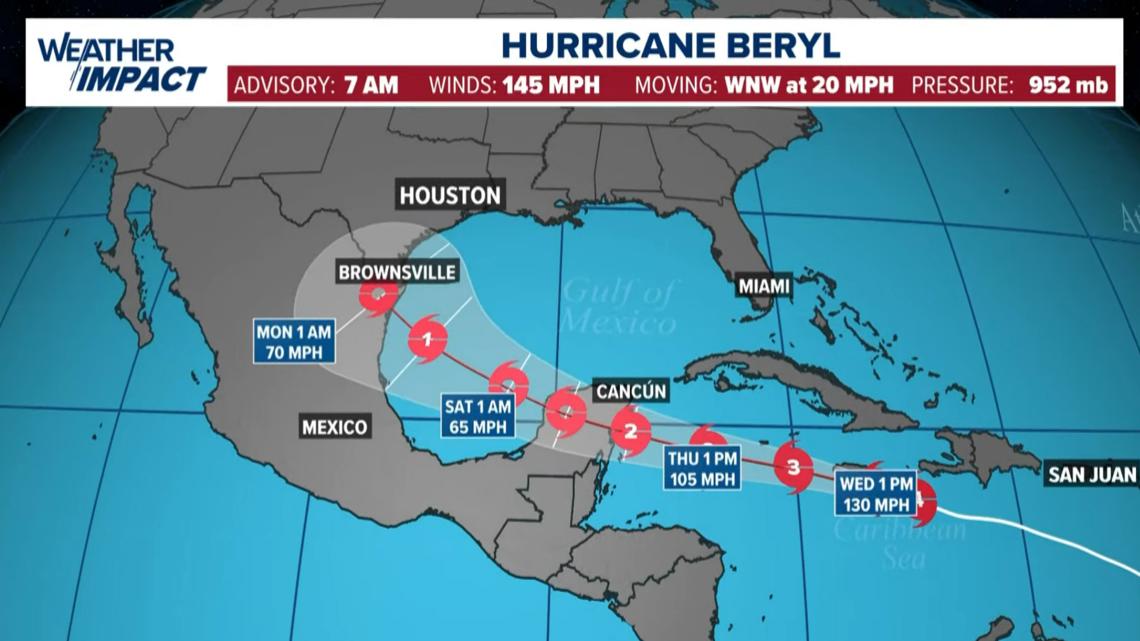
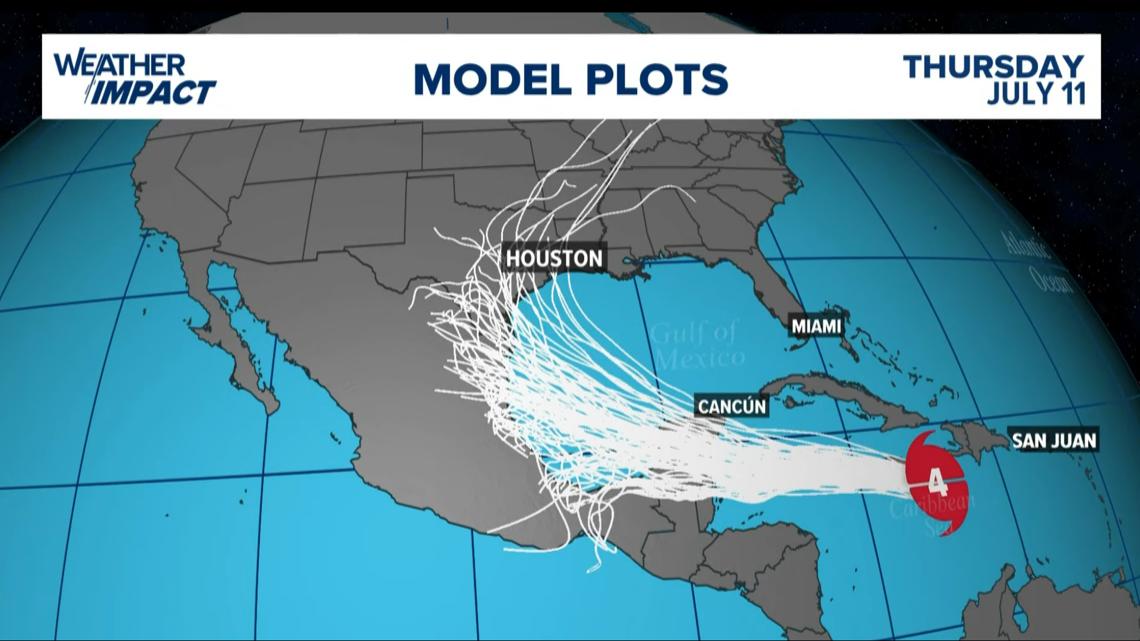
The forecast track from the Hurricane Center takes the storm into the Yucatan, then back into the Gulf of Mexico as a much-weakened tropical storm. If this forecast verifies, Houston/Galveston would see minimal impacts -- increased chance for scattered showers, minor coastal flooding, beach erosion and rip currents, much like what Alberto did in June.
The storm is still a long way out and forecasts can change. Watch the weather multiple times a day this week so no one gets caught off guard if things change with this well-organized storm. There’s a lot of uncertainly with the forecast as Beryl enters the Gulf so Texans should keep a close eye on updates throughout the week
CURRENT LOCATION/PATH: With the 7 a.m. Wednesday update, Beryl was a Category 4 storm with maximum sustained winds of 145 mph, moving west-northwest at 20 mph. (Update in Spanish).
Hurricane Beryl forecast cone

Hurricane Beryl spaghetti models

RELATED: KHOU 11 Chief Meteorologist David Paul on what Texans should be watching with Hurricane Beryl
You can see Chief Meteorologist David Paul's 10 p.m. Tuesday forecast here.
Hurricane Season links
Track the storm
Hurricane season 2024 forecast
Colorado State University released its forecast update for the 2024 hurricane season, maintaining that it will be a busy one. In April, they predicted that we could see 23 named storms and 11 hurricanes with five becoming major hurricanes. They blame the extremely warm tropical Atlantic and likely “La Niña” as the primary reasons.
RELATED: Colorado State University releases hurricane season forecast update, maintains it will be a busy one
On average, the Atlantic sees about 14 named storms each hurricane season. Of those, seven become hurricanes with three becoming major (Category 3 or above) storms.
Why such an active season? Dr. Phil Klotzbach, lead forecaster at CSU, says it's because of two main factors -- above-normal sea surface temperatures and expected La Niña conditions this summer. The warm water adds more energy to the tropics, making fuel for these storms more available. But perhaps more importantly, La Niña usually reduces vertical wind shear.
Winds blowing across a developing or mature tropical system can keep a budding system from developing and weaken stronger storms. This reduces the total storm count. But when La Niña conditions are in place, this wind shear is often reduced. That, combined with the warm ocean surface temps is why Dr. Klotzbach believes more storms than normal will form.



