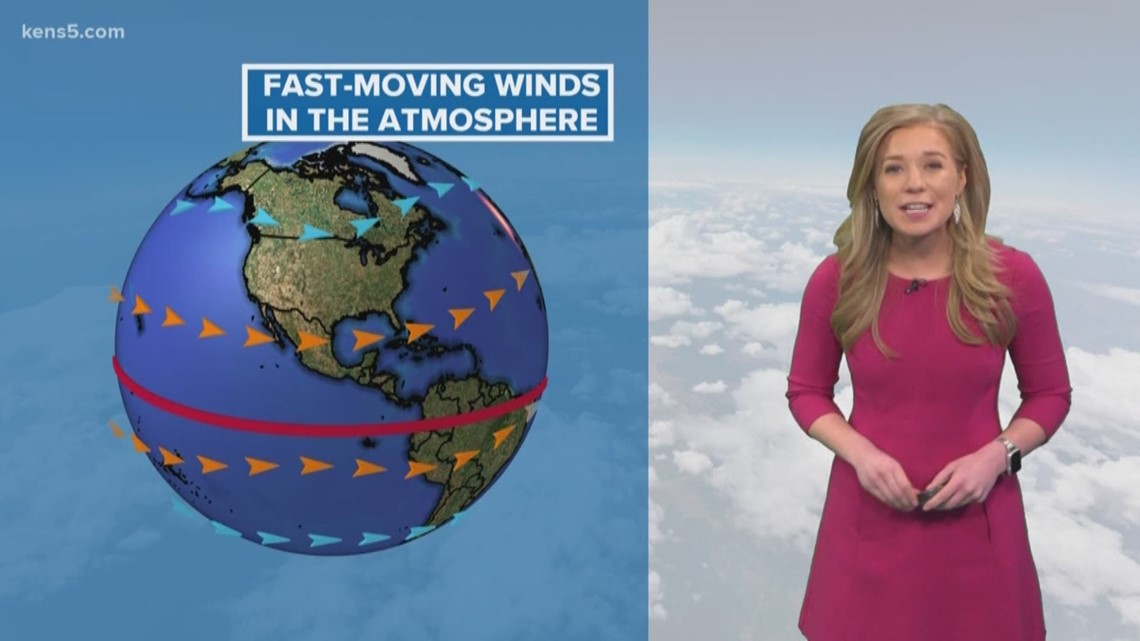
SAN ANTONIO — Jet streams are responsible for changes in weather across the world. Think of it this way: Jet streams are fast-moving rivers in the upper levels of the atmosphere.
They can impact air travel and many other things that take place in the mid-to-upper troposphere. There are four types of jet streams over the Earth, which include two polar jets stream near the poles and two subtropical jet streams closer to the equator.
Each jet stream consists of high-winds that blow from west to east, but the flow will shift from north to south.
How do jet streams form?
It starts with warm air masses meeting cold air masses. The sun does not heat the Earth equally, which is why it is cooler over the poles and warmer closer to the equator.
Warm air will rise into the atmosphere while cold air sinks to replace the warm air, creating a current of wind. It also depends on where high pressure and low pressure systems are located.
Jet streams can range from four to nine miles above the Earth's surface.
According to NOAA, on average, a jet stream will move at about 110 miles per hour. However, big temperature differences can cause jet streams to move up to 250 miles per hour or greater. That is one fast jet stream!
RELATED:
How do jet streams affect our weather?
The narrow bands of strong wind can nudge weather systems across the United States. These systems can bring rain, wintry weather, and changes in temperature. Sometimes weather disturbances can not get caught up in the jet stream, which can cause the system to get stuck and sit in one area. This can lead to flooding, a heatwave, or sometimes record snowfall events. Meteorologists utilize satellites in space, like GOES-R, to see jet streams.
By observing jet streams over the globe, meteorologists can monitor weather systems and see where these disturbances are going.
Don't forget you can download the KENS 5 app for the latest news and weather information each day while you are on the go.
PEOPLE ARE ALSO READING: